Intellectual Property
Intellectual property, also known as IP, describes an item or idea that has been credited as belonging to somebody in some way. Common types of IPs would be patented or copyrighted materials.
Intelligence
Fraud Intelligence is the leading practical resource for the counter-fraud professional; it provides applied insight, analysis and tools to combat fraud and corruption, whether in the corporate or non-commercial sector, together with coverage of relevant statute and case law.
Intelligence Augmention
Intelligence Augmentation, or IA, is an alternative conceptualization of artificial intelligence that focuses on AI's assistive role, emphasizing the fact that cognitive technology is designed to enhance human intelligence rather than replace it. The choice of the word augmented, which means "to improve," reinforces the role human intelligence plays when using machine learning and deep learning algorithms to discover relationships and solve problems.
Internal Fraud (Insider Fraud)
What is Insider Fraud?
Insider fraud refers to fraudulent activities committed within an organization by individuals with access to sensitive information, systems, or resources due to their positions within the company. These individuals could be employees, contractors, vendors, or anyone with internal access. Insider fraud can involve various illicit activities, such as embezzlement, theft, data breaches, intellectual property theft, and more.
Some statistics related to insider fraud: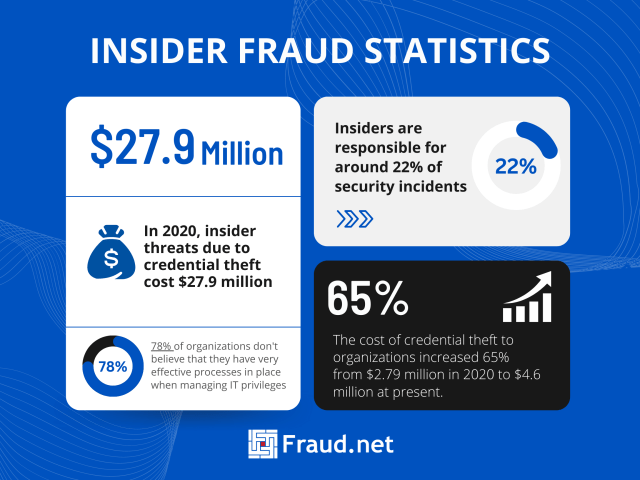
- In 2020, insider threats due to credential theft cost $27.9 million
- The cost of credential theft to organizations increased 65% from $2.79 million in 2020 to $4.6 million in 2022
- Insiders are responsible for around 22% of security incidents
- 78% of organizations don’t believe that they have very effective processes in place when managing IT privileges
Common Types of Insider Fraud
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, various forms of illicit activities have emerged, each targeting valuable assets and personal information. Embezzlement stands as a grave concern, involving the diversion of funds or resources meant for legitimate purposes for one’s personal enrichment. This misappropriation not only undermines the integrity of financial systems but also erodes trust within organizations and communities.
Another prevalent threat is data theft, where individuals or groups unlawfully breach security measures to access and abscond with sensitive information. This stolen data can be exploited for personal gain or even sold on the black market, causing severe financial and reputational damage to the affected individuals or entities.
Moreover, intellectual property theft exacerbates these challenges by undermining innovation and creativity. Unauthorized replication or distribution of proprietary data or trade secrets deprives rightful owners of their hard-earned intellectual assets, hampering progress and hindering healthy competition within industries. Furthermore, identity fraud compounds these issues as stolen identities or credentials are exploited to gain unauthorized access to resources, perpetrate fraudulent schemes, and wreak havoc on individuals’ financial and personal lives.
Insider fraud differs from external fraud in that it involves individuals with some level of trust and access within the organization. External fraud is perpetrated by outside actors with no direct affiliation with the organization. While external fraud often requires bypassing security measures, insider fraud takes advantage of the perpetrator’s legitimate access
Solutions for Insider Fraud
Addressing insider fraud requires a combination of strategies:
- Employee Screening: Thorough background checks and continuous monitoring can identify potential risks during the hiring process and throughout employment.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit individuals’ access to sensitive systems and data only to the extent necessary for their roles.
- Regular Auditing: Conduct routine audits of financial and operational activities to detect anomalies or suspicious patterns.
- Whistleblower Programs: Create a safe environment for employees to report suspicious activities without fear of retaliation.
- Security Training: Provide regular training to employees about security best practices, fraud indicators, and the consequences of insider fraud.
- Behavioral Analytics: Utilize advanced analytics to identify unusual behaviors and flag potentially fraudulent activities.
- Clear Policies: Establish clear guidelines for handling sensitive information, conflicts of interest, and acceptable use of company resources.
Fraud.net’s Solution
Fraud.net offers an AI-powered fraud prevention solution that includes specific features to combat insider fraud:
Modern security systems leverage advanced technologies to safeguard against insider fraud and unauthorized data breaches. User Behavior Analysis lies at the core of these systems, diligently observing user actions to swiftly pinpoint deviations from established norms. By discerning unusual behaviors, this approach efficiently detects suspicious insider activities, mitigating potential risks. Complementing this, Anomaly Detection employs cutting-edge machine learning algorithms to meticulously identify atypical patterns and actions that could signify insider fraud. This analytical prowess serves as a formidable defense against emerging threats.
To fortify defenses further, Data Leakage Prevention takes charge of tracking sensitive information’s movement. Through vigilant monitoring, it effectively thwarts unauthorized data transfers, safeguarding against potential breaches. A swift response is key, and the system excels in this aspect with Real-time Alerts. These instantaneous notifications promptly notify relevant parties upon the detection of suspicious activities, enabling immediate intervention. Additionally, Compliance Monitoring plays a vital role, in ensuring adherence to industry regulations and internal protocols. By upholding these standards, it diligently uproots opportunities for insider fraud to take root, fostering a secure environment.
To learn more about how Fraud.net’s AI-driven solution can help safeguard your organization against insider fraud, we invite you to request a demo or book a consultation with our experts. Protect your business from the threats posed by insider fraud today.
Interoperability
Interoperability describes the ability of computer systems or software to exchange and make use of information. Interoperability requires mechanical compatibility among the systems, and it is only able to take results from where profitable contracts have been settled among the systems.

