B2B (Business-to-Business)
B2B or Business-to-Business refers to a business that sells products or provides services to other businesses.
B2C (Business-to-Consumer)
B2C or Business-to-Consumer refers to a business that sells products or provides services to the end-user consumers. Another variation of this concept is D2C (direct to consumer) in which a manufacturer sells directly to consumers with little to no intermediation.
Back Door
A route through which legitimate users or criminals can bypass security systems in order to access the data they’re after. Contrasts with a front door attack, where a virus or attack is done with help from the user, for instance by downloading an infected email attachment.
Baiting
Baiting describes the situation where a fraudster leaves something out like a USB drive, enticing somebody to pick it up and see what content is on it. The fraudster loads the USB drive up with things like malware and keyloggers, which attack a computer system when plugged in. This scheme is designed to take advantage of people’s curiosity.
Bank Identification Number (BIN Number)
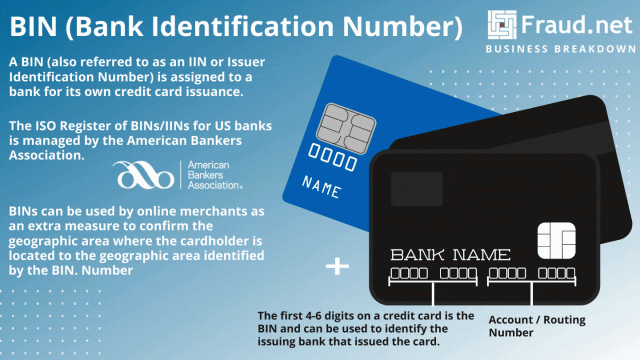
A BIN Number or Bank Identification Number is assigned to a bank for its own credit card issuance.
The first six digits on a credit card constitute the Bank Identification Number, otherwise known as the BIN number. A BIN identifies the institution that issues the credit or debit card. The American Bankers Association manages the ISO Register of BINs and Issuer Identification Numbers(IINs) for US banks. Online merchants use BINs (Bank Identification Numbers) as an extra measure to confirm the geographic area where the cardholder is located. For instance, they compare it to the geographic area identified by the unique BIN number. Occasionally, some refer to BIN Numbers as an IIN or Issuer Identification Number.
BIN Attack Fraud
One way fraudsters use BIN numbers is in scams known as BIN Attack Fraud. The fraudster obtains a BIN and uses software to generate the remaining numbers. They then test the numbers using small transactions through online retailers until they find a valid and active card number.
Common signs of a BIN attack:
- Multiple low-value transactions that are unusual for your business
- Multiple declines
- Unusually high volumes of international cards
- Large quantity of transactions being processed or attempted in a short period of time
- Card numbers being used repeatedly with variations in the security features
- Unusual transaction times
Protect Against Fraud
Businesses and institutions can protect themselves against fraudsters using techniques like BIN attacks with an adaptive and responsive fraud protection platform.
Fraud.net offers a variety of solutions using AI and machine learning to prevent fraud attacks of all kinds and therefore, your bottom line. We offer dark web monitoring, analytics and reporting, identity protection services, and more.
Contact us for a demo and recommendations for fraud prevention and identity protection.
Learn More
Bitcoin
The most famous and popular cryptocurrency. While it is often thought of as an anonymous payment method, bitcoin (BTC) is actually pseudonymous, which means it is possible to track someone’s payments if you can tie a real life identity to a BTC wallet.
Burn(er) Phone
The term originates from the drug dealing world, and is used to describe inexpensive mobile phones designed for temporary use. It allows fraudsters and criminals to link an account to a disposable phone number, for instance to bypass 2FA.
Today, phone numbers can be generated via burner phone apps or services. These work like prepaid phone cards, only allowing you to use them for a limited amount of time before being recirculated. Because they go through your phone’s original cellular data, they can be traced.

